
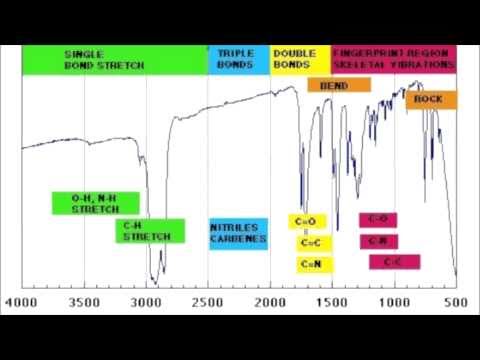
The following web-sites provide nice collections of problems and answers: The button on the right will activate a collection of problems concerning the reactivity of common functional groups. Most organic chemistry textbooks contain a broad assortment of suitable problems, and paperback collections of practice problems are also available. Since problem solving is essential to achieving an effective mastery of the subject, it is recommended that many more problems be worked. To practice using this editor Click Here. Some of these problems make use of a Molecular Editor drawing application created by Peter.Ertl of the Novartis Corp.

The practice problems provided as part of this text are chiefly interactive, and should provide a useful assessment of the reader's understanding at various stages in the development of the subject. Reactions at the α Carbon Acidity of α C–H The Claisen Condensation Synthesis ApplicationsĪt various points throughout this text, links to supplementary information or special topics will be located in shaded boxes of this kind. Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Acyl Group Substitution Mechanism Reduction Catalytic Reduction Metal Hydride Reduction Diborane Reduction Reaction with Organometallic Reagents Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Salt Formation Substitution of Hydroxyl Hydrogen Substitution of the Hydroxyl Group Reactions at the α-Carbon Mechanism of Electrophilic α-Substitution The Aldol Reaction Ambident Enolate Anions Alkylation of Enolate Anions Irreversible Addition Reactions Complex Metal Hydrides Organometallic ReagentsĬarbonyl Group Modification Wolff-Kishner Reduction Clemmensen Reduction Hydrogenolysis of Thioacetals Oxidations Reversible Addition Reactions Hydration & Hemiacetal Formation Acetal Formation Imine Formation Enamine Formation Cyanohydrin Formation Occurrence of Aldehydes & Ketones Natural Products Synthetic Preparation Reactions of Aryl Diazonium Intermediates Practice Problems Reactions with Nitrous Acid Reactions of Amines Electrophilic Substitution at Nitrogen Preparation of 1º-Amines Preparation of 2º & 3º-Amines Properties of Amines Boiling Point & Solubility Basicity of Nitrogen Compounds Acidity of Nitrogen Compounds Important Reagent Bases Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination & Addition Reactions Reactions of Ethers Acid Cleavage Peroxide Formation Epoxide ReactionsĮlectrophilic Substitution A Substitution Mechanism Reactions of Substituted Benzenes Reaction Characteristics Reactions of Disubstituted Rings Reactions of Substituent Groups Reactions of Phenols Acidity of Phenols Ring Substitution of Phenols Oxidation to Quinones Reactions of Alcohols Substitution of the Hydroxyl H Substitution of the Hydroxyl Group Elimination of Water ( HO H) Oxidation of Alcohols Substitution(of X) S N2 Mechanism S N1 MechanismĮlimination (of HX) Summary of Substiution vs.
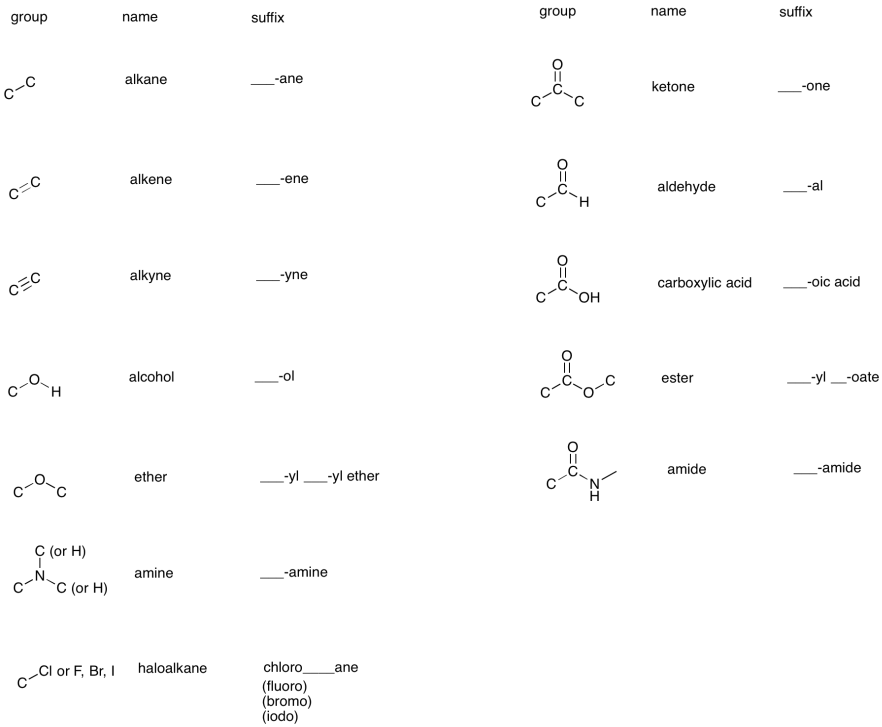
The alkanes are relatively unreactive, and provide a background of behavior in the absence of more localized functional groups.Įlectrophilic Additions Strong Brønsted Acids Lewis Acids (non-Proton Electrophiles) Electrophilic Halogen Reagents Other Electrophilic Reagents Reduction Oxidationĭienes Addition Reactions Diels-Alder CycloadditionĪcidity of Terminal Alkynes (Substitution of H) The following table summarizes the general chemical behavior of the common functional groups. Because of this, the discussion of organic reactions is often organized according to functional groups. A particular functional group will almost always display its characteristic chemical behavior when it is present in a compound. Chemical Reactivity Functional Group ReactionsĬharacteristic Reactions of Functional Groupsįunctional groups are atoms or small groups of atoms (two to four) that exhibit a characteristic reactivity when treated with certain reagents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
